저번 시간에는 서버같은 서버를 만들어보았다.
오늘은 이 시리즈의 마지막 편으로, Django 와 android 의 서버 통신에 대해 알아보겠다.
(android studio 사용 언어 : kotlin )
먼저 django 에서 urls 에 아래 코드를 추가해보자.
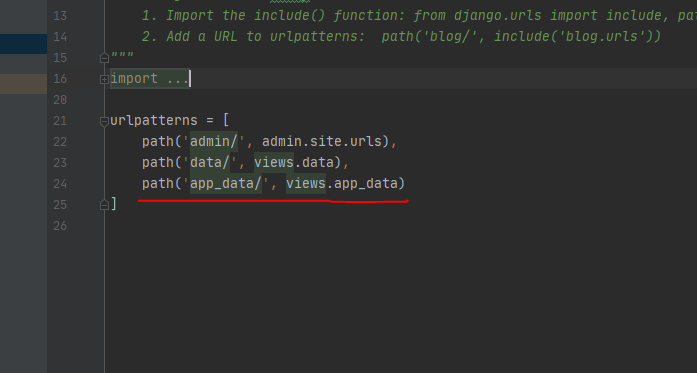
앱에서는 다르게 처리를 할 것이기 때문에 urls 에 위의 코드를 추가한 것이다.
에러가 나도 놀라지 말자. 아직 views 안에 app_data 함수를 추가하지 않았기 때문이다.
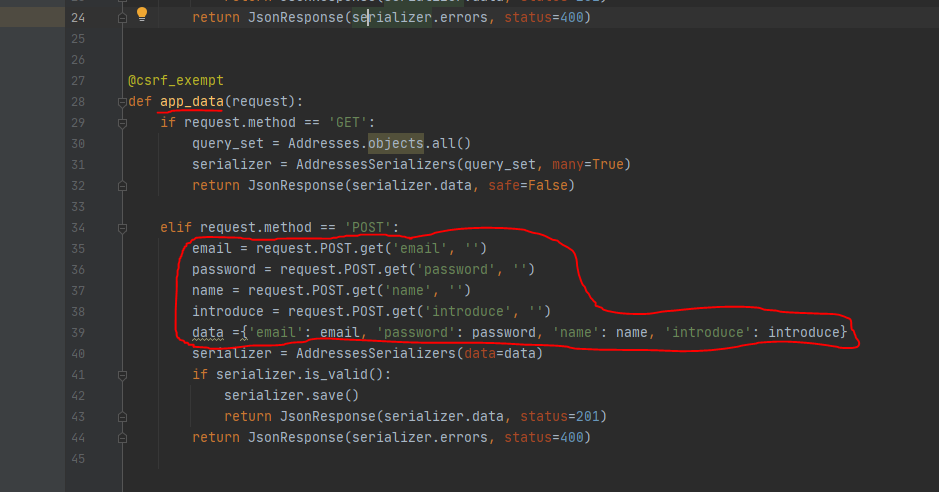
저번 시간에 만들었던 data 코드를 복사+붙여넣기 하여 빨간색 부분만 수정해주도록 하자.
앱에서는 Json 으로 받아오기 힘들기 때문에 다르게 처리를 해주는 것이다.
자 이제 서버 부분은 끝이 났다.
android studio 에서 새로운 project 를 만들어보자.
project 를 만들었으면 아래 사진처럼 두줄을 추가해주자.
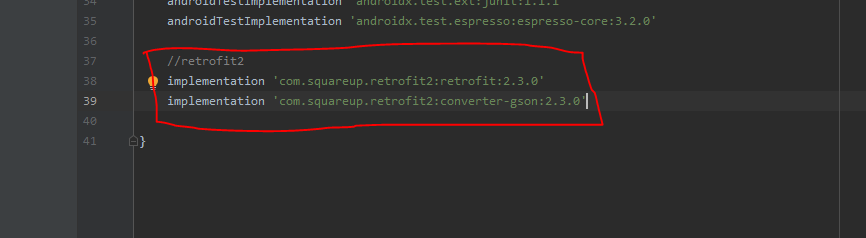
오른쪽 위에 Sync now 를 눌러 Sync 도 하자.
자 이제 ApiService interface 를 만들어보자.
아래 사진처럼 코드를 추가하자.
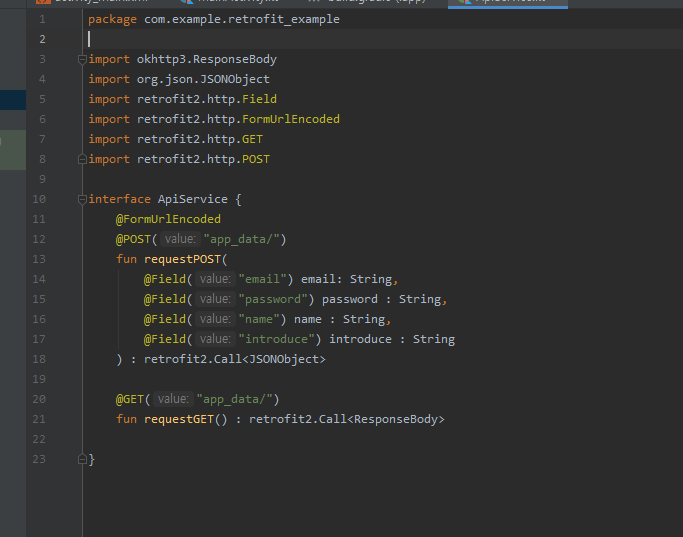
12번째 줄같은 경우에는 POST 로 baseUrl을 기준으로 app_data/ 에 보낸다는 뜻이다.
뭘? -> email, password, name, introduce 를.
20번 같은 경우네느 마찬가지로 GET 으로 baseUrl을 기준으로 app_data/ 에 보낸다는 뜻이다.
뭘로? -> ResponseBody 로.
자 그럼 이제는 activity_main.xml 을 꾸며주자.
//activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="email"
android:id="@+id/email_edit"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="password"
android:id="@+id/password_edit"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/email_edit"
/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="name"
android:id="@+id/name_edit"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/password_edit"/>
<EditText
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="introduce"
android:id="@+id/introduce_edit"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/name_edit"/>
<Button
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/introduce_edit"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="16dp"
android:id="@+id/post_btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="POST"/>
<Button
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/introduce_edit"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp"
android:layout_marginRight="16dp"
android:id="@+id/get_btn"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="GET"/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:id="@+id/get_text"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/get_btn"
/>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
그럼 이제 MainActivity 차례다!
//MainActivity.kt
package com.example.retrofit_example
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import android.os.Bundle
import android.util.Log
import android.widget.Toast
import kotlinx.android.synthetic.main.activity_main.*
import okhttp3.ResponseBody
import org.json.JSONObject
import retrofit2.Call
import retrofit2.Response
import retrofit2.Retrofit
import retrofit2.converter.gson.GsonConverterFactory
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
lateinit var retrofit : Retrofit
lateinit var apiService : ApiService
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
val baseUrl = "https://90f5045a42c0.ngrok.io"
retrofit = Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(baseUrl)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.build()
apiService = retrofit.create(ApiService::class.java)
post_btn.setOnClickListener {
val email = email_edit.text.toString()
val password = password_edit.text.toString()
val name = name_edit.text.toString()
val introduce = introduce_edit.text.toString()
apiService.requestPOST(email, password, name, introduce).enqueue(object : retrofit2.Callback<JSONObject>{
override fun onResponse(call: Call<JSONObject>, response: Response<JSONObject>) {
Toast.makeText(applicationContext, "POST 성공", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
}
override fun onFailure(call: Call<JSONObject>, t: Throwable) {
Log.d("TAG", t.message)
}
})
}
get_btn.setOnClickListener {
apiService.requestGET().enqueue(object : retrofit2.Callback<ResponseBody>{
override fun onResponse(call: Call<ResponseBody>, response: Response<ResponseBody>) {
get_text.text = response.body()!!.string()
}
override fun onFailure(call: Call<ResponseBody>, t: Throwable) {
Log.d("TAG", t.message)
}
})
}
}
}
자 코드가 너무 복잡해보인다고 어려워 하지 말자.
하나하나 설명을 해주겠다.
lateinit var retrofit : Retrofit
lateinit var apiService : ApiService
처음에 lateinit var 로 변수를 선언하였다.
lateinit 은 나중에 정의하겠다는 뜻이다.
그렇기에 onCreate 되었을 때 정의를 한것이다.
val baseUrl = "https://90f5045a42c0.ngrok.io"
이 부분이 중요하다.
https://90f5045a42c0.ngrok.io 이것처럼 따라하지 말고.
먼저 아래 사이트로 가서 ngrok 을 다운을 받자.
ngrok - download
Running this command will add your authtoken to your ngrok.yml file. Connecting an account will list your open tunnels in the dashboard, give you longer tunnel timeouts, and more. Visit the dashboard to get your auth token.
ngrok.com
다운로드를 받았다면 설치된 디렉토리로 이동해서
아래 사진처럼 ngrok http 8000 을 입력해보자.
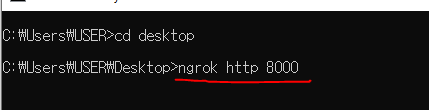
입력을 하게 되면, 아래 사진처럼 뜨게 될텐데 내가 드래그 한 부분을 복사를 하자.
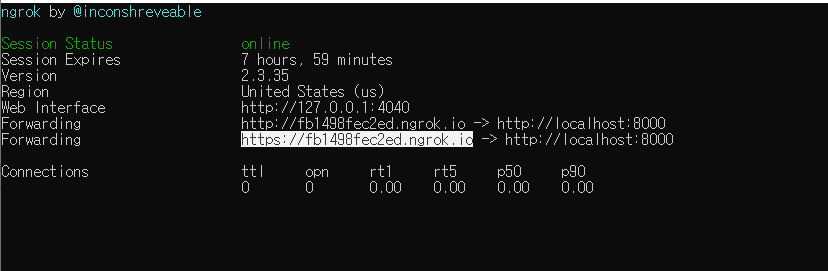
저 부분이 이제 baseUrl 로 들어가는 것이다.
post_btn.setOnClickListener {
val email = email_edit.text.toString()
val password = password_edit.text.toString()
val name = name_edit.text.toString()
val introduce = introduce_edit.text.toString()
apiService.requestPOST(email, password, name, introduce).enqueue(object : retrofit2.Callback<JSONObject>{
override fun onResponse(call: Call<JSONObject>, response: Response<JSONObject>) {
Toast.makeText(applicationContext, "POST 성공", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
}
override fun onFailure(call: Call<JSONObject>, t: Throwable) {
Log.d("TAG", t.message)
}
})
}
이 부분은 email, password, name, introduce 변수에 유저가 입력한 각각 데이터를 대입하고,
apiService 안에 있는 requestPOST 에 데이터를 넣어서 보낸다.
그리고 override fun onResponse 에서는 성공을 했을 때 실행되는 부분이고,
onFailure 는 실패했을 때 실행되는 부분이다.
get_btn.setOnClickListener {
apiService.requestGET().enqueue(object : retrofit2.Callback<ResponseBody>{
override fun onResponse(call: Call<ResponseBody>, response: Response<ResponseBody>) {
get_text.text = response.body()!!.string()
}
override fun onFailure(call: Call<ResponseBody>, t: Throwable) {
Log.d("TAG", t.message)
}
})
}
이 부분은 apiService 안에 requestGET 을 실행하는 것이다.
마찬가지로 성공을 했다면 받은 데이터를 get_text의 text 로 표시하는 것이고,
실패를 했다면 에러를 Log 에 찍는 것이다.
자 이제 준비는 모두 끝났으니 django 에서
python manage.py runserver 명령어를 이용하여 server 를 실행하고,
앱을 실행해보자.
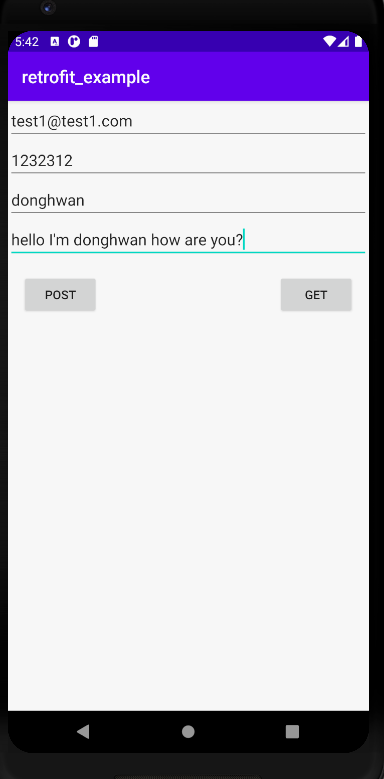
데이터를 입력하고, POST 버튼을 눌러보자.
(주의 : email 은 40자, password 는 20자, name 은 10자 이내로 입력해야 한다.)
그러면 POST 성공이라는 메세지가 뜰 것이다.
이제 GET 버튼을 눌러보자.
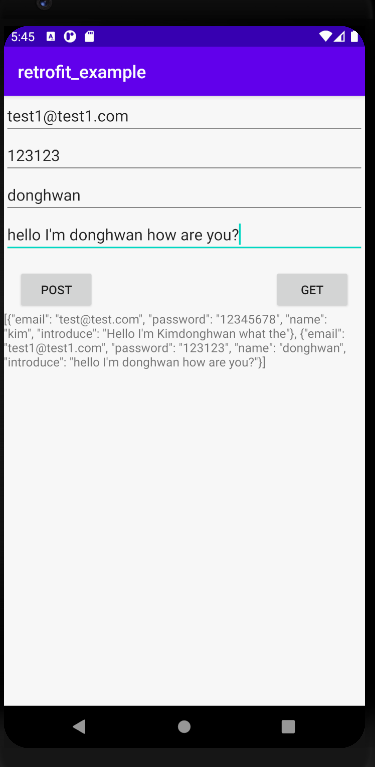
저번에 저장했었던 데이터까지 같이 불러와졌다. o0o
보기가 불편하지만 데이터를 가지고 왔다는 것이 중요하다.
핵심 요약!
1. retrofit 을 이용하면 android 와 Django 가 서로 통신을 할 수 있다.
(retrofit 말고도 다른 것들 많음)
2. android 가 서버와 통신하는 것은 생각보다 쉽다!
이번편을 마지막으로 이번 시리즈는 끝이 났다.
더 공부를 하고 싶은 독자는 열심히 구글링을 해보며 원하는 무언가를 만들어내었으면 좋겠다.
'retrofit 을 이용한 Django, android 서버 통신' 카테고리의 다른 글
| retrofit 을 이용한 Django, android 서버 통신 (2) (0) | 2020.08.08 |
|---|---|
| retrofit 을 이용한 Django, android 서버 통신 (1) (0) | 2020.08.08 |

